
EMR and PACS Integration: A Third-Party Vendor's Perspective
April 14, 2024
Introduction
Navigating the landscape of interoperability in healthcare presents a unique set of challenges for third-party vendors, especially those specializing in cloud-based solutions. The core of these challenges lies in establishing seamless connectivity with health information systems like EHR (Electronic Health Records) and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems). In this post, we discuss challenges as well as practical strategies and solutions to integrate healthcare provider systems.
First, let’s talk about the Challenges
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of different healthcare information systems, devices and applications to communicate and exchange data with each other in a seamless and coordinated manner. Interoperability has been a major initiative across the world for many years but it’s still a difficult landscape.
At any large healthcare organization, connecting on-premise healthcare data inside the network requires a time consuming project with the assistance and coordination of numerous teams. Sending that data outside the network to third-party vendor cloud services poses an additional new set of challenges primarily around connectivity options and cybersecurity processes.
To add to the confusion, most engineering teams are not familiar with the many technical and practical challenges in healthcare data exchange.
List of Challenges in Connecting with Healthcare Organizations
- Cybersecurity in Healthcare: Healthcare is a heavily regulated industry and there are strict rules and guidelines that must be followed when connecting to healthcare provider systems. Identifying and implementing the correct measures can be difficult and time consuming.
- Compatibility: Different healthcare providers may use different electronic health record (EHR) systems and other healthcare information technology systems, which can make it difficult to ensure that your product will work seamlessly with all of them.
- Integration time and cost: Integrating with healthcare provider systems can be time-consuming and expensive, and the process may require significant resources from both the vendor and the provider.

Overcoming the Hurdles
There are a number of products and services on the market aimed at helping you tackle the various hurdles we’ve outlined above. Let’s discuss a few of these and how they’re used in a real world setting.
Interface Engines
Ensure that your product is able to integrate seamlessly with healthcare providers by taking advantage of industry standard healthcare interface engines. Interface engines are software platforms that enable connectivity and exchange of data between different healthcare systems. You can think of it like an interpreter helping your systems speak with the hospital.
Some key technical features:
- Data transformation: Transform data from one format to another, making it easier to integrate with different healthcare systems.
- Message routing: Route messages between different systems based on pre-defined rules, ensuring that the right information is sent to the right place.
- Data encryption and security: Built-in data encryption and security features to protect sensitive health information.
- Monitoring and logging: Monitor and log the flow of information between systems, making it easier to troubleshoot any issues.
A Practical Example: Mirth Connect
Mirth Connect is the most popular open-source healthcare integration engine providing a high-level platform for the exchange and transformation of healthcare data.
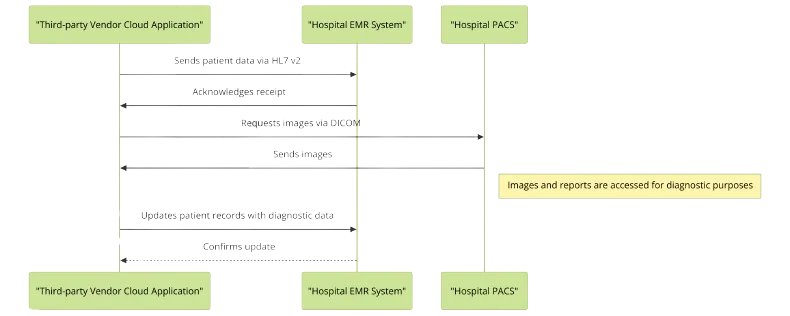
How does an interface engine connect to healthcare provider EMR, PACS, HIE’s and other systems?
Healthcare organizations all have their own specific preferences and technical capabilities. Below, an architectural diagram outlines some of the popular connectivity methods, followed by a technical overview. Remember, a third-party vendor may need to support multiple integration pathways to connect with different healthcare organizations.
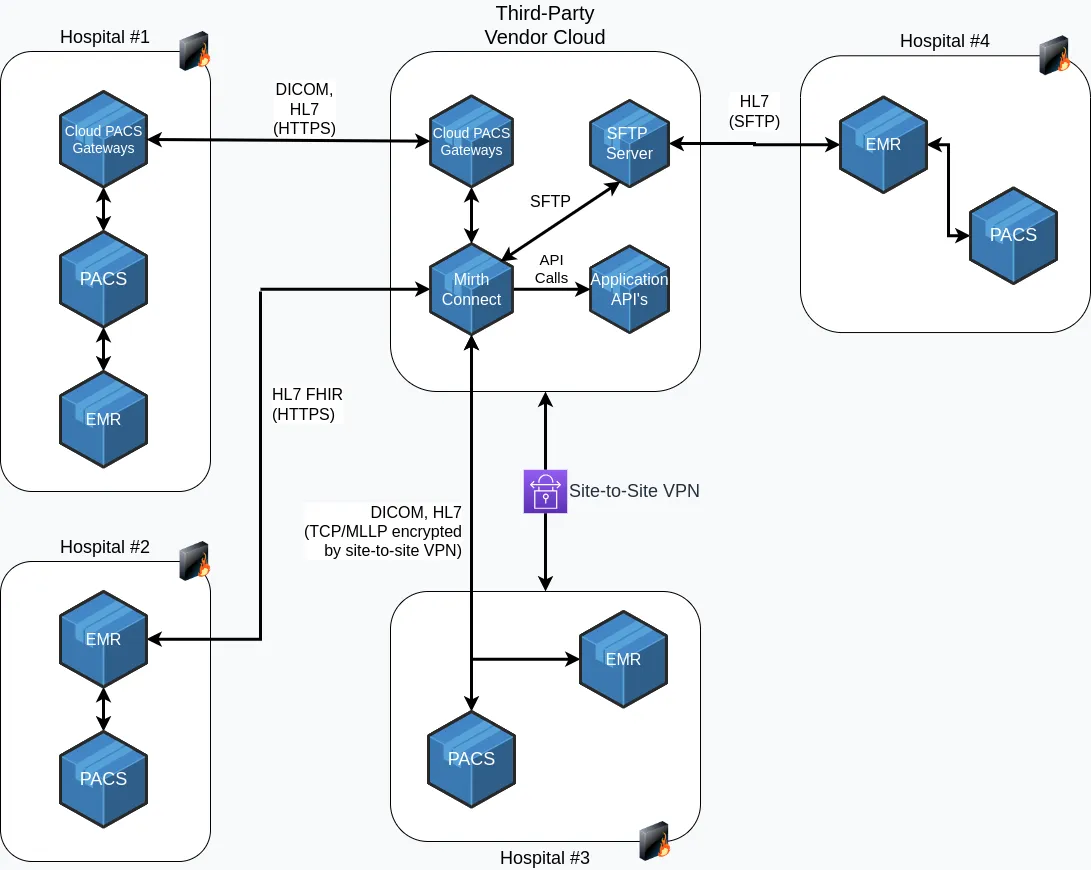
1. Site-to-site VPN with HL7 v2 & DICOM
Site-to-site VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): Site-to-site are used frequently in healthcare. They provide a means to secure unencrypted data such as HL7, DICOM and other sensitive healthcare data.
HL7 v2 (Health Level Seven Version 2): HL7 v2 is a widely used messaging standard for exchanging healthcare information between different computer systems. Some of the advantages of HL7 v2 include:
Wide Adoption: HL7 v2 has been widely adopted and is used across most healthcare organizations, making it a well-established and widely recognized standard.
Scalability: Capable of handling large volumes of data, making it suitable for use in large healthcare organizations and national health information networks.
Rich Data Model: Provides a rich data model that can handle a wide range of healthcare data types, including patient demographics, clinical information, and laboratory results.
Legacy System Support: HL7 v2 has been in use for several decades, making it a well-established standard that is well-suited for integration with legacy systems.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine): The universal format for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting medical images. DICOM-DIMSE (DICOM Protocol for Message Exchange) is a protocol used in the DICOM standard to enable the exchange of medical images between different computer systems. Some of the advantages of DICOM include:
Wide Adoption: DICOM has been used across the industry for many years, making it a well-established universal standard in medical imaging (unlike the rest of healthcare data).
Support for Large Image Data Sets: Designed to handle large image data sets, making it suitable for use in large healthcare organizations and for the storage of large medical images such as MRI and CT scans.
Support for Multiple Modalities: Supports a wide range of imaging modalities, including X-ray, MRI, CT, PET, and ultrasound, making it a flexible solution for handling medical images.
2. Connecting with HL7 FHIR
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is the newest standard for healthcare information exchange from HL7. Some of the features of FHIR include:
Web Protocols: FHIR uses modern web technologies. It’s an HTTP-based RESTful protocol with a full set of standardized REST APIs.
Security: Encryption in transit via HTTPS (SSL/TLS) solves the security issues associated with older HL7 versions (which are plaintext).
SMART on FHIR: Provides a consistent, secure, and standardized way to authorize, authenticate, and communicate with health data servers.
Cost-effectiveness: FHIR can reduce the costs associated with implementing and maintaining older integration pathways.
3. Cloud PACS Gateway
A cloud PACS gateway is software that allows medical imaging data to be stored, retrieved, and viewed from a cloud-based platform. It acts as a bridge between a local PACS system and the cloud, facilitating the transfer of medical images typically in the format DICOM. The purpose of the cloud PACS gateway is to provide healthcare organizations with a secure, scalable, and cost-effective solution for storing, sharing, and accessing medical imaging data as well as HL7 messages.
4. SFTP Server
SFTP is frequently used to transmit DICOM, HL7 and other various message types because it provides a secure and reliable method for exchanging large amounts of data between different computer systems. SFTP is a secure version of FTP (File Transfer Protocol), which encrypts both the data being transmitted and the control information used to manage the transfer, providing a secure channel for transmitting sensitive medical information.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex landscape of healthcare data integration requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific challenges and the deployment of strategic solutions. With the appropriate healthcare domain technologies, your product can more easily be deployed and integrated with healthcare provider systems.
If you need help and want to learn more about our services and how we partner with organizations to optimize integration with healthcare providers:
READING DONE
